Have you ever wondered why trampolines make you soar so high? The thrill of bouncing effortlessly into the air is more than just fun—it’s a fascinating interplay of physics and engineering. In this blog, we’ll uncover the science behind that exhilarating bounce, exploring the components and principles that make trampolines work. From the tension in the springs to the elasticity of the mat, let’s dive into the mechanics that turn a simple jump into a sky-high adventure.
The Basic Components of a Trampoline
To understand what makes family trampolines bounce, let’s start by exploring their basic components. Each part plays a crucial role in creating that perfect jump.
Frame
The frame of a trampoline is its backbone. Typically made from galvanized steel, the frame provides the stability and strength necessary to support the entire structure.
- Structure and Material: Most frames are made of heavy-duty steel, chosen for its durability and resistance to rust. The frame’s design ensures it can withstand repeated impacts and the weight of multiple jumpers.
- Importance of Stability and Strength: A sturdy frame is essential for safety and performance. It keeps the trampoline stable, preventing it from tipping over or collapsing during use.
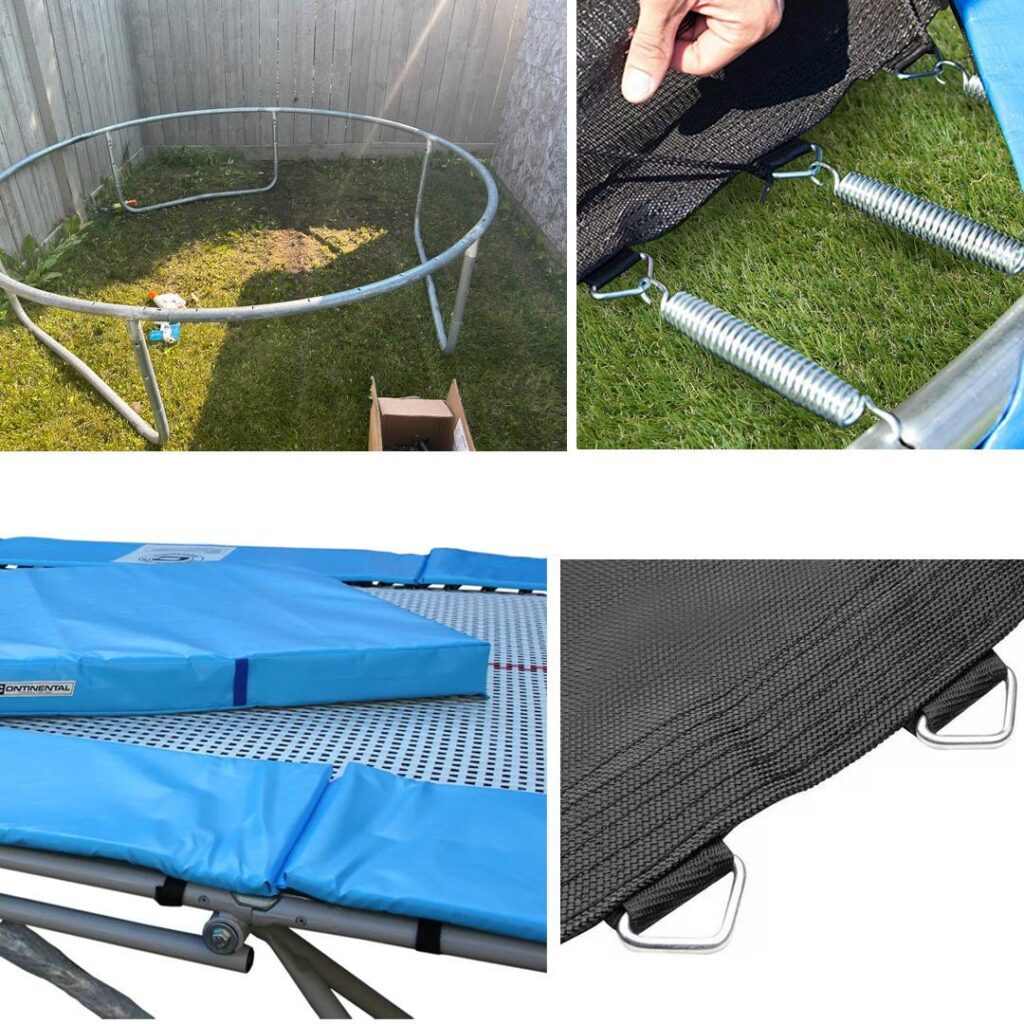

Springs
The springs are the secret behind the trampoline’s bounce.
- Contribution to Bounce: Springs store and release energy, which propels the jumper into the air. When you jump, the springs stretch and then quickly return to their original shape, converting potential energy into kinetic energy.
- Types of Springs:
- Coiled Springs: These are the most common and are known for their strong, consistent bounce.
- Bungee Cords: Used in some modern trampolines, bungee cords offer a softer bounce and are less likely to cause injuries.
Jumping Mat
The jumping mat is where the action happens.
- Material and Properties: Made from woven polypropylene or nylon, the mat is designed to be both strong and flexible. These materials can withstand UV rays and heavy use without tearing.
- Role of Tension: The mat is tightly stretched across the frame, held in place by the springs. This tension is crucial for the trampoline’s performance, allowing the mat to provide a responsive and lively bounce.
Safety Pads and Nets
Safety is a top priority in trampoline design.
- Safety Pads: These pads cover the springs and frame, preventing jumpers from getting injured by the hard metal or pinching their skin in the springs. Typically made from foam and vinyl, they provide a cushioned barrier.
- Safety Nets: Surrounding the jumping area, safety nets prevent users from falling off the trampoline. Made from high-strength netting, these enclosures are designed to withstand impacts and keep jumpers safely contained.
The Science of Bouncing

Now that we’ve covered the basic components of a trampoline, let’s dive into the science that makes public use trampolines bounce. Understanding the principles of physics involved can make your trampoline experience even more fascinating.
Elastic Potential Energy
When you jump on a trampoline, you’re engaging with elastic potential energy.
- Definition and Explanation: Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object when it is stretched or compressed. In the case of a trampoline, both the mat and the springs store this type of energy.
- How the Mat and Springs Store Energy: As you jump, your weight pushes down on the mat, causing it to stretch. Simultaneously, the springs are stretched and store energy. The more you compress the mat and springs, the more energy is stored, ready to be released as you bounce back up.
Kinetic Energy
The stored energy in the trampoline needs to convert to kinetic energy to propel you upwards.
- Conversion to Kinetic Energy: Once the mat and springs reach their maximum stretch and begin to return to their original state, the stored elastic potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. This conversion propels you upwards, with the amount of kinetic energy determining how high you bounce.
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
Newton’s Third Law of Motion plays a crucial role in the bouncing process.
- Action-Reaction Principle: Newton’s Third Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When you push down on the trampoline mat (action), the mat pushes back with equal force (reaction), propelling you into the air. This interaction is what makes jumping on a trampoline so dynamic and exhilarating.
Hooke’s Law
Hooke’s Law explains the relationship between the force applied to the springs and the displacement they experience.
- Brief Explanation of Hooke’s Law: Hooke’s Law states that the force needed to extend or compress a spring is directly proportional to the distance it is stretched or compressed. Mathematically, it is expressed as 𝐹=−𝑘𝑥F=−kx, where 𝐹F is the force applied, 𝑘k is the spring constant, and 𝑥x is the displacement.
- Relevance to Springs: In a trampoline, Hooke’s Law helps us understand how the springs react to the force of your jump. The stiffer the springs (higher 𝑘k value), the more force is required to stretch them, which in turn influences the height and responsiveness of the bounce.
Factors Influencing Bounce

Several factors influence how high and efficiently you can bounce on a trampoline. Understanding these can help you optimize your sport trampoline experience.
Spring Quality and Tension
The quality and tension of the springs are crucial for a good bounce.
- How Different Tensions and Spring Quality Affect the Bounce: High-quality springs made from durable materials provide a consistent and strong bounce. The tension in the springs determines how much they stretch and contract. Tighter springs store more elastic potential energy, leading to a higher bounce. Conversely, worn-out or loose springs will not provide the same level of energy return, resulting in a lower and less responsive bounce.
Mat Material and Elasticity
The material and elasticity of the jumping mat significantly impact energy transfer.
- Impact of Different Materials on the Efficiency of Energy Transfer: Mats made from high-quality, woven polypropylene or nylon are both strong and flexible, allowing for efficient energy transfer. These materials can stretch sufficiently to store energy and then return to their original shape, propelling the jumper upwards. Cheaper or less elastic materials may not perform as well, reducing the height and efficiency of the bounce.
User’s Weight and Jumping Technique
The jumper’s weight and technique also play vital roles in bounce dynamics.
- How Weight and Technique Influence Bounce Height and Efficiency: Heavier users compress the mat and spring more, storing more elastic potential energy, which can result in a higher bounce. However, if the trampoline is not designed to support its weight, it can lead to reduced performance and potential damage. The jumping technique is equally important; jumping straight up and down maximizes energy transfer, while erratic or uneven jumping can dissipate energy and reduce bounce height.
Weather Conditions
Environmental factors like temperature and humidity can affect trampoline performance.
- Effects of Temperature and Humidity on Trampoline Performance: In colder temperatures, springs, and mats can become stiffer, reducing their elasticity and the height of the bounce. In contrast, warmer temperatures can make the materials more flexible, enhancing performance. High humidity can affect the mat’s material, making it heavier and less responsive. Proper maintenance and storage can mitigate some of these weather-related effects.
Innovations in Trampoline Design

Trampoline design has come a long way, with advancements in materials and technology enhancing both performance and safety. Let’s explore some of the latest innovations that are revolutionizing the above & in-ground trampoline experience.
Advancements in Materials
Trampoline manufacturers are continually exploring new materials and technologies to improve bounce and safety.
- New Materials: Innovations in material science have led to the development of high-performance fabrics and polymers that are stronger, more durable, and more elastic than ever before. These materials enhance the bounce and longevity of trampolines, providing a more enjoyable and safer experience for users.
- Technological Enhancements: Advanced coatings and treatments improve UV resistance, weatherproofing, and anti-slip properties, ensuring that trampolines can withstand the elements and remain safe and functional for years to come.
Safety Innovations
Safety is always a top priority in trampoline design, and manufacturers are constantly innovating to reduce the risk of injuries.
- Impact Absorption Systems: Advanced padding and cushioning materials help absorb impact forces, reducing the risk of injury in the event of a fall or collision. These systems provide a softer landing surface and minimize the risk of bruises, scrapes, and fractures.
- Enclosure Systems: Modern trampolines are equipped with high-strength safety nets and enclosures that surround the jumping area, preventing users from falling off the trampoline. These nets are designed to withstand heavy impacts and provide a secure barrier, giving users peace of mind while bouncing.
Fascinating Trampoline Facts and Trivia

Trampolines have a rich history and a wide range of fascinating applications beyond recreational bouncing. Let’s explore some fun facts and trivia that highlight the versatility and excitement of trampolines.
Historical Facts
Trampolines have evolved from their humble beginnings to become a beloved recreational activity worldwide.
- Origin: The modern trampoline traces its roots back to 1936 when George Nissen and Larry Griswold, two American gymnasts, invented the first trampoline in their garage. They were inspired by trapeze artists using safety nets to perform aerial stunts.
- Evolution: Trampolines gained popularity as training tools for gymnasts and acrobats before transitioning into recreational equipment for backyard fun. Today, trampolines are enjoyed by people of all ages and are even used for fitness and rehabilitation purposes.
World Records
Trampolining has produced some incredible feats and record-breaking achievements.
- Notable Records: The highest bounce on a trampoline, the longest continuous bouncing session, and the most flips performed in a minute are just a few of the impressive records set by trampoline enthusiasts around the world.
- Olympic Achievements: Trampolining became an Olympic sport in 2000, showcasing the athleticism and skill of competitors from various countries. Olympic trampoline events feature jaw-dropping routines filled with flips, twists, and somersaults.
Unusual Uses
Trampolines have found surprising applications beyond the realm of recreation.
- Space Training: NASA has used trampolines to simulate the effects of weightlessness experienced by astronauts in space. Training on trampolines helps astronauts develop their balance, coordination, and spatial awareness in a gravity-free environment.
- Performance Arts: Trampolines have become integral to various performance arts, including circus acts, theater productions, and stunt shows. Performers use trampolines to execute gravity-defying jumps, flips, and aerial tricks that captivate audiences around the world.
Various factors play a role in selecting the right trampoline for both children and adults. If you’re an adult contemplating purchasing a trampoline, it’s crucial to explore which ones are currently recognized as the top choices among adults. By gaining insight into the best and most sought-after options, you can make a wise decision that suits your needs and preferences
Conclusion
Trampolines are not just for bouncing; they’re a fascinating blend of science, innovation, and history. From the mechanics of bounce to record-breaking achievements and unexpected uses like space training, the world of trampolining is full of surprises. So, the next time you take a jump, remember the rich tapestry of excitement that trampolines offer. Keep exploring and enjoying the thrill of the bounce!